Overview
Specifications
Supported Versions
The Authenticator supports iOS 12 and above
Authorization Server Requirements
Authorization servers should not require clients maintain client secrets. Clients should opt for Universal Links as a redirect. PCKE support is coming soon to mitigate risk using a Custom URL Scheme.
Setup
Swift Package Manager
With Swift Package Manager,
add the following dependency to your Package.swift:
dependencies: [
.package(url: "https://github.com/gobeyondidentity/bi-sdk-swift.git", from: "<<ios-sdk-embedded-version>>")
]
Run swift build
Usage
Currently, Beyond Identity only supports clients with a backend. This allows for two flows:
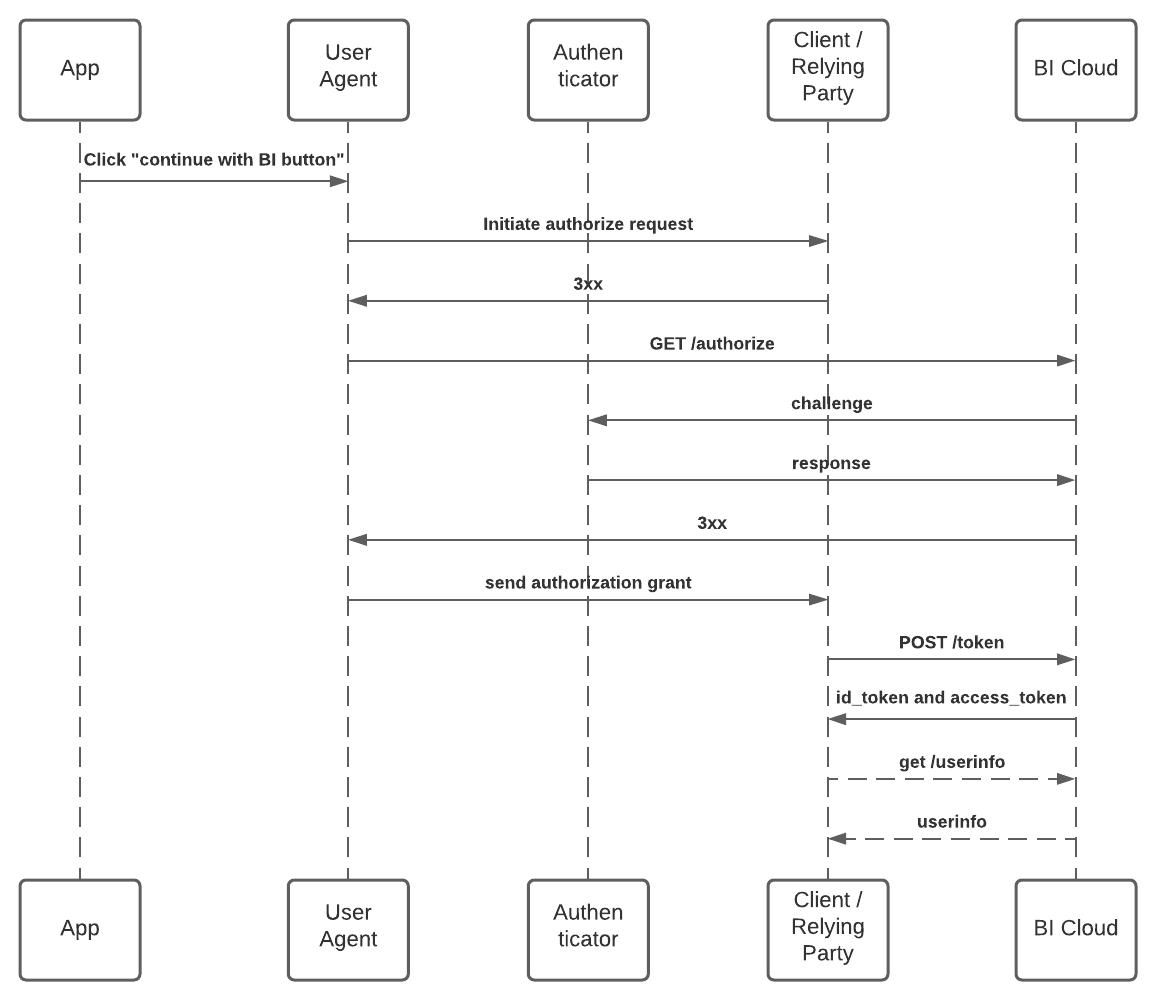
- Client / Relying Party Initiated Flow
The confidential client (backend) is configured to get the authorization code and exchange that code for an access token and id token.
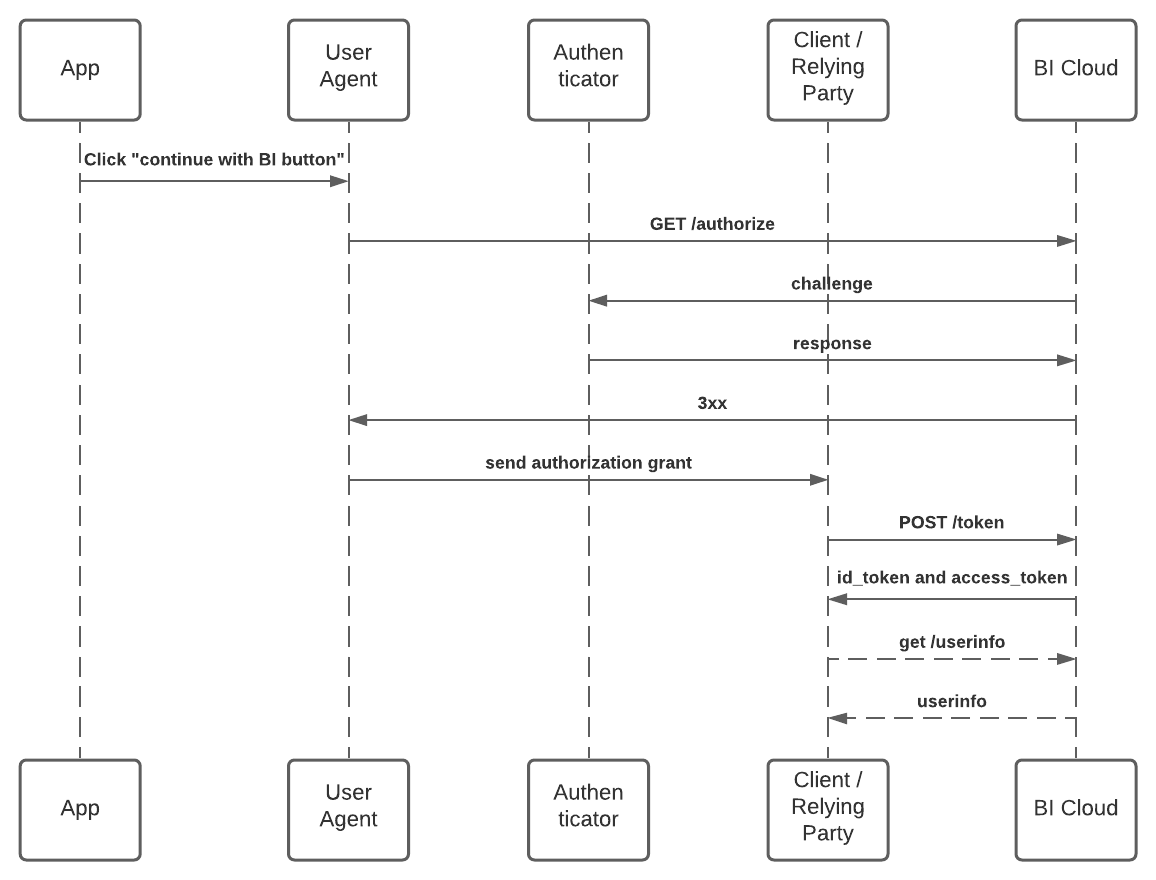
- Direct Initiated Flow
The public client (mobile app) queries for the authorization code and your confidential client (backend) makes the token exchange.
View Setup
For either flow you'll want to create and add an AuthView in your ViewController. This view contains both Beyond Identity Sign In and Sign Up buttons.
When the user taps the "Sign In" button, an instance of ASWebAuthenticationSession is created and will start. A secure, embedded web view loads and displays the page, from which the user can authenticate. When the user taps "Sign Up" button the AuthView will trigger your sign up action.
The AuthView accepts five parameters. This first four are parameters from ASWebAuthenticationSession.
url: A URL with the http or https scheme pointing to the authentication webpage.callbackURLScheme: The custom URL scheme that the app expects in the callback URL.completionHandler: A completion handler the session calls when it completes successfully, or when the user cancels the session.prefersEphemeralWebBrowserSession: A Boolean value that indicates whether the session should ask the browser for a private authentication session. Set to true to request that the browser doesn’t share cookies or other browsing data between the authentication session and the user’s normal browser session. The value of this property is false by default.signUpAction: A closure triggered when the user taps the AuthView "Sign Up" button. Your sign up action should include a call to the Beyond Identity API to create a user credential as well as a way for the user to download the Beyond Identity App to store the credential associated with your app.
warning
Custom Schemes offer a potential attack as iOS allows any URL Scheme to be claimed by multiple apps and thus malicious apps can hijack sensitive data.
When configuting ASWebAuthenticationSession
use a Universal Link for the callbackURLScheme to mitigate risk.
Client / Relying Party Initiated Flow
In this scenerio your confidential client (backend) handles getting the authorization code and exchanging that for an access token and id token.
It is up to the developer to decide how to invoke their confidential client in order to initiate the flow, as well as what the response would be. As an example, a response could be a session id associated with the authenticated user or the userinfo payload that was queried on the confidential client.
Initialize an AuthView with a url that points to the authentication webpage that you have configured your confidential client. A secure, embedded web view loads and displays the page, from which the user can authenticate.
On completion, the service sends a callback url to the registered redirect with an authentication token or anything else you have configured your confidential client to send in that url. In order to intercept that callback, provide a ASWebAuthenticationSession.CompletionHandler to the completionHandler parameter.
Depending on how you configured your redirect, you may need to provide a callbackURLScheme.
import BeyondIdentityAuthenticator
/* ! WARNING !
Custom Schemes offer a potential attack as iOS allows any
URL Scheme to be claimed by multiple apps and thus malicious
apps can hijack sensitive data.
To mitigate this risk, use Universal Links in your production app.
*/
let authView = AuthView(
url: viewModel.cloudURL,
callbackURLScheme: viewModel.urlScheme,
completionHandler: { [weak self] url, error in
if let error = error { self?.signInCallBack(.failure(error)) }
if let url = url { self?.signInCallBack(.success(url)) }
},
signUpAction: signUpAction
)
view.addSubview(authView)
func mySignUpAction() {
<!-- call to Beyond Identity API to create a user -->
}
Direct Initiated Flow
In this scenerio your public client (mobile app) handles getting the authorization code and your confidential client (backend) handles exchanging that code for an access token and id token.
It is up to the developer to decide what the response would be for your confidential client. As an example, a response could be a session id associated with the authenticated user or the userinfo payload that was queried on the confidential client.
The Beyond Identity /authorize endpoint supports the following parameters:
client_id: unique ID for a tenant's registered OIDC client.redirect_uri: must match one of the configured values for the client.response_type: Onlycodesupported at this time.scope: must containopenid(except for OAuth2).state: random string that the client can use to maintain state between the request and the callback.
Initialize an AuthView with a url that points to Beyond Identity's /authorize endpoint with the appropriate parameters. A secure, embedded web view loads and displays the page, from which the user can authenticate.
On completion, the service sends a callback url to the session. In order to intercept that callback, provide a ASWebAuthenticationSession.CompletionHandler to the completionHandler parameter. You'll need to confirm the state parameter has not changed and then pass the authorization code to your backend to exchange for an access token and id token.
import BeyondIdentityAuthenticator
/* ! WARNING !
Custom Schemes offer a potential attack as iOS allows any
URL Scheme to be claimed by multiple apps and thus malicious
apps can hijack sensitive data.
To mitigate this risk, use Universal Links in your production app.
*/
self.state = UUID().uuidString
var authorizeEndpoint = URLComponents(string: "https://auth.byndid.com/v2/authorize")!
authorizeEndpoint.queryItems = [
URLQueryItem(name: "client_id", value: viewModel.kClientId),
URLQueryItem(name: "redirect_uri", value: viewModel.urlScheme),
URLQueryItem(name: "state", value: self.state),
URLQueryItem(name: "response_type", value: "code"),
URLQueryItem(name: "scope", value: "openid")
]
let authView = AuthView(
url: authorizeEndpoint.url!,
callbackURLScheme: nil,
completionHandler: { url, error in
if let error = error { print(error) }
if let url = url { print(url) }
// Check the state matches the state you've sent
guard let url = url, let currentState = url.queryParameters?["state"],
currentState == self.state! else {
// someone is interfering with our auth process
return
}
guard let url = url, let components = URLComponents(url: url, resolvingAgainstBaseURL: true),
components.queryItems?.first(where: { $0.name == "state" })?.value == self.state! else {
return
}
if let code = components.queryItems?.first(where: { $0.name == "code" })?.value {
// Exchange the authorization code for access token and id token
print(code)
}
},
signUpAction: signUpAction
)
view.addSubview(authView)
func mySignUpAction() {
<!-- call to Beyond Identity API to create a user -->
}
Prerequisites
Since most of the heavy lifting is delegated to the Beyond Identity Authenticator client when integrating the Authenticator SDK you need to download the app on your development phone (you'll need the App Store).